There are a couple of ways to get your credit score, including a loan statement, credit card bill, a non-profit or by paying a small fee to one of the credit bureaus.
Each person has more than one credit score. Credit scores are based on your credit history and how well you have paid other forms of credit and debt in the past from cell phone bills, household bills, credit cards and even payday loans.
If the information at each credit agency is different then your credit score could be slightly different with each organization. Each lender uses different credit scores for different types of loans.
Four Main Ways To Get Your Credit Score
1. Your credit card or loan statement
Many of the big credit card companies, and some of the auto loan companies, have begun to show your credit score on your monthly statement. This score is usually listed when you get your account balance at the end of the month or it can be found by logging on to their online portal.
2. Talk to a not-for-profit counsellor
A non-profit credit counsellor or a HUD-approved housing counsellor is often able to give you a free credit score and help talk you through what the key elements mean.
3. Use a credit score bureau
If you do a quick search in Google you’ll find lots of websites that advertise a free credit score. Some of these websites are funded through advertising and so do not charge a fee to you. Other websites make you sign up for their monthly service exchange for receiving your credit score.
Lots of companies offer a free trial but then if you don’t cancel after the trial, you’ll be paid a monthly subscription fee. Sometimes the free trial is only one week long so make sure to pay attention closely to their terms and conditions. Before you try one of these services make sure you know what you’re actually signing up for, how much it will cost, and what the cancellation terms are.
4. Buy your credit score
The final option is to buy your score directly from the credit reporting bureaus. You can buy your FICO score at myfico.com. There are other companies that will offer your credit score for sale too. If you want to see your credit score then you don’t have to also buy purchase credit protection or identity theft monitoring, products that are regularly offered at the same time.
Some sources provide a credit score for education purposes. This is different to a credit score that a lender would use. The CFB published a report on the difference between a credit score used by lenders and the credit score used for education. For most situations, an educational credit score will be enough information and is similar enough to the one used by lenders. For others, the score can be quite different.
Key Points
- There are different ways to find out your credit score
- You can check your credit card or loan statement, use a credit score bureau or talk to a non-profit counselor
- If you are worried about your credit score, there are different ways to build credit
What Goes Into My Free Credit Score?
When you or a lender check your credit score a methodology from either FICO or VantageScore will be applied to your credit history. Your score will vary depending on which VantageScore or FICO version was used. It will also depend on whether they get your report from Equifax, Experian or TransUnion. Your credit score can vary day to day and month to month based on these factors.
If you have a good Vantage SCORE then you probably have a good FICO score. Both will be influenced by taking steps to improve your credit score. This is because they consider similar factors but have slightly different methodologies.
The factors they take into account are:
Payment history – this is how regularly you make payments on time and whether you have any negative marks on your payment history. This also includes any accounts sent to bankruptcy or collections.
Credit utilization – this is how much money you owe and how much of your available credit you’re using.
Age of credit history – this is how long you’ve been using credit
Number of applications – the frequency you’ve applied for credit
Type of credit – what kinds of credit accounts and how many you have. This includes installment loans (mortgage or car loans), credit cards or a mix
What Doesn’t Go Into My Credit Score
A credit score does not take into account how much you make each month, your savings or job security. This is why, in addition to your credit score, lenders look at these factors when making a decision on whether to loan you money.
What Can I Do With My Credit rating?
When you have a high credit rating you have a better chance of qualifying for credit cards and loans with the best interest rates. If you have good credit it can also save you money. This is because you may qualify for better cell phone deals, pay smaller deposits on your utilities, and pay less for insurance for your car or home. Some landlords and employers even consider credit history when offering you a job.
There are many ways to build better credit; a score of over 800 is an “excellent” credit score.
What is a Good Credit Score?
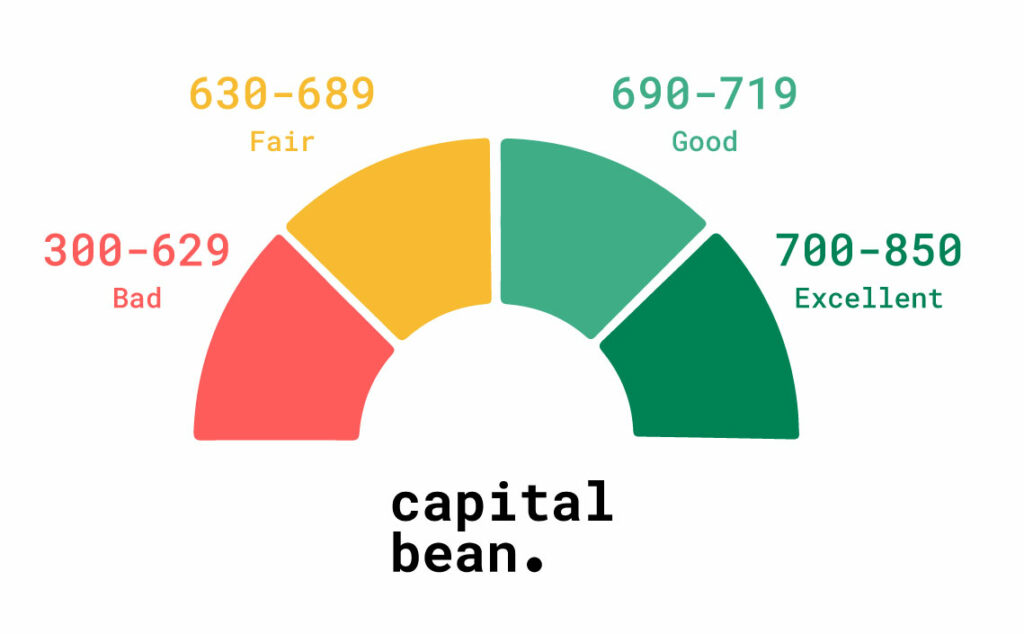
The most common credit score range is from 300 to 850. Anything over 800 is excellent. Each lender has its own standard for what constitutes a good credit score. In general, the following brackets are used:
- Excellent credit: 720+
- Good credit: 690-719
- Fair credit: 630-689
- Bad credit: 629 and below
 How Can I Increase My Credit Score?
How Can I Increase My Credit Score?
The two largest factors in a good credit score are paying your bills on time and managing your credit utilization rate.
Other important recommendations include:
Make sure to pay all of your bills, not just your credit cards, on time each month. Any late payments or accounts that are sent to collections agencies will hurt your credit.
Use no more than 30% of the credit available on any card. Try to stay under 30% in all cases. The very best scores go to those that are using under 10% of their available credit.
Keep accounts open and active if possible. By keeping your accounts open and not bouncing between credit cards you’ll establish a good history and background.
Don’t open too many new accounts at the same time. Every time you open a new account it will lower your average account age. It will also cause a small ding to appear on your score each time you open an account. We would suggest spacing credit applications at least 6 months apart as this is best practice. Make sure to research which credit card is the best option for you before applying.
Check your credit report for errors. Before applying for a new product get a copy of your credit report and read through it closely. Look out for any accounts that you don’t have any more or misreported data on the report.



